The Microsoft Compatibility Telemetry process is a crucial part of Windows operating systems, designed to collect and send data back to Microsoft. While this data collection helps Microsoft improve its products and services, it can sometimes lead to high CPU usage, causing performance issues on your computer. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the causes of this problem, provide solutions, and offer optimization tips to keep your system running smoothly.
What is Microsoft Compatibility Telemetry?
Microsoft Compatibility Telemetry is a feature in Windows that collects technical data about your device and its software. This data includes details about how your hardware and software are functioning, error reports, and system performance statistics. The primary purpose of this telemetry is to help Microsoft identify issues, enhance system performance, and deliver better user experiences in future updates.
Why Does Microsoft Compatibility Telemetry Cause High CPU Usage?
There are several reasons why Microsoft Compatibility Telemetry might lead to high CPU usage:
- Large Volume of Data: The telemetry process can sometimes handle a large amount of data, which demands more processing power.
- Background Scanning: Telemetry often runs background scans to gather data, which can spike CPU usage.
- Outdated or Corrupted Files: If there are outdated or corrupted system files, the telemetry process may struggle, leading to increased CPU usage.
- Windows Updates: Sometimes, after a Windows update, the telemetry process might become more active, temporarily increasing CPU usage.
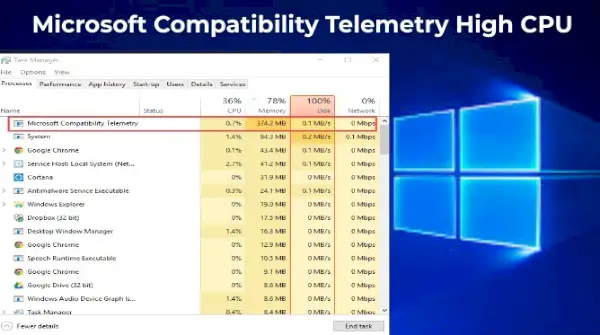
How to Check if Microsoft Compatibility Telemetry is Causing High CPU Usage
To determine whether Microsoft Compatibility Telemetry is using a significant amount of CPU resources, follow these steps:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open the Task Manager.
- Click on the Processes tab.
- Look for CompatTelRunner.exe or Microsoft Compatibility Telemetry in the list.
- Check the CPU usage column to see if it’s consuming a high percentage of your CPU.
Methods to Fix High CPU Usage Caused by Microsoft Compatibility Telemetry
If you find that Microsoft Compatibility Telemetry is indeed using a high amount of CPU, you can try the following solutions:
1. Disable Microsoft Compatibility Telemetry
One of the most effective ways to reduce CPU usage is to disable the telemetry process. Here’s how you can do it:
- Press Win + R to open the Run dialog.
- Type gpedit.msc and press Enter to open the Group Policy Editor.
- Navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Data Collection and Preview Builds.
- Double-click on Allow Telemetry.
- Select Disabled, then click Apply and OK.
2. Use Registry Editor to Disable Telemetry
If you don’t have access to the Group Policy Editor (usually on Windows Home editions), you can disable telemetry using the Registry Editor:
- Press Win + R and type regedit to open the Registry Editor.
- Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\DataCollection.
- Double-click on Allow Telemetry (if it doesn’t exist, create a new DWORD value with this name).
- Set the value to 0 and click OK.
3. Update Your System
Sometimes, high CPU usage can be due to outdated system files. Keeping your Windows operating system up-to-date can resolve these issues:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security.
- Click on Check for updates.
- Install any available updates and restart your computer.
4. Use Disk Cleanup
Clearing out unnecessary files on your system can help reduce the load on your CPU:
- Press Win + S and type Disk Cleanup.
- Select your system drive (usually C:).
- Check all the boxes and click OK to delete the files.
5. Run the Windows Troubleshooter
Windows has a built-in troubleshooter that can help resolve issues related to high CPU usage:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot.
- Select Additional troubleshooters.
- Run the Windows Update troubleshooter and follow the on-screen instructions.
Optimizing System Performance Beyond Telemetry Issues
Once you’ve dealt with the high CPU usage caused by Microsoft Compatibility Telemetry, you might want to take additional steps to optimize your system’s performance. Here are some tips:
1. Manage Startup Programs
Too many programs starting up with Windows can slow down your system. You can manage these programs through the Task Manager:
- Open Task Manager with Ctrl + Shift + Esc.
- Click on the Startup tab.
- Disable unnecessary programs by right-clicking and selecting Disable.
2. Upgrade Your Hardware
If your system is still struggling with high CPU usage, it might be time to consider upgrading your hardware. Adding more RAM or switching to a solid-state drive (SSD) can significantly boost performance.
Understanding the Different Levels of Telemetry in Windows
Windows allows users to choose from different levels of telemetry data collection. Understanding these levels can help you make an informed decision about which level to set:
| Telemetry Level | Description |
|---|---|
| Basic | Collects basic data necessary to keep Windows secure and up-to-date. |
| Enhanced | Collects additional data, including how Windows and apps are used, to improve the user experience. |
| Full | Collects the most comprehensive data set, including all data from Basic and Enhanced, along with diagnostic data. |
Impact of Telemetry on Privacy and Security
While Microsoft Compatibility Telemetry is essential for improving Windows, it raises concerns about privacy and security. Here are some considerations:
- Data Collection: Understand what data is being collected and how it’s used.
- Privacy Settings: Adjust your privacy settings to control what information is sent to Microsoft.
- Third-Party Tools: Consider using third-party tools to block telemetry data if privacy is a major concern.
Microsoft Compatibility Telemetry is a vital component of Windows, but it can sometimes lead to high CPU usage, affecting your system’s performance. By understanding what causes this issue and applying the solutions provided in this guide, you can optimize your system and maintain a smooth computing experience. Remember to regularly update your system, manage startup programs, and consider hardware upgrades if necessary.