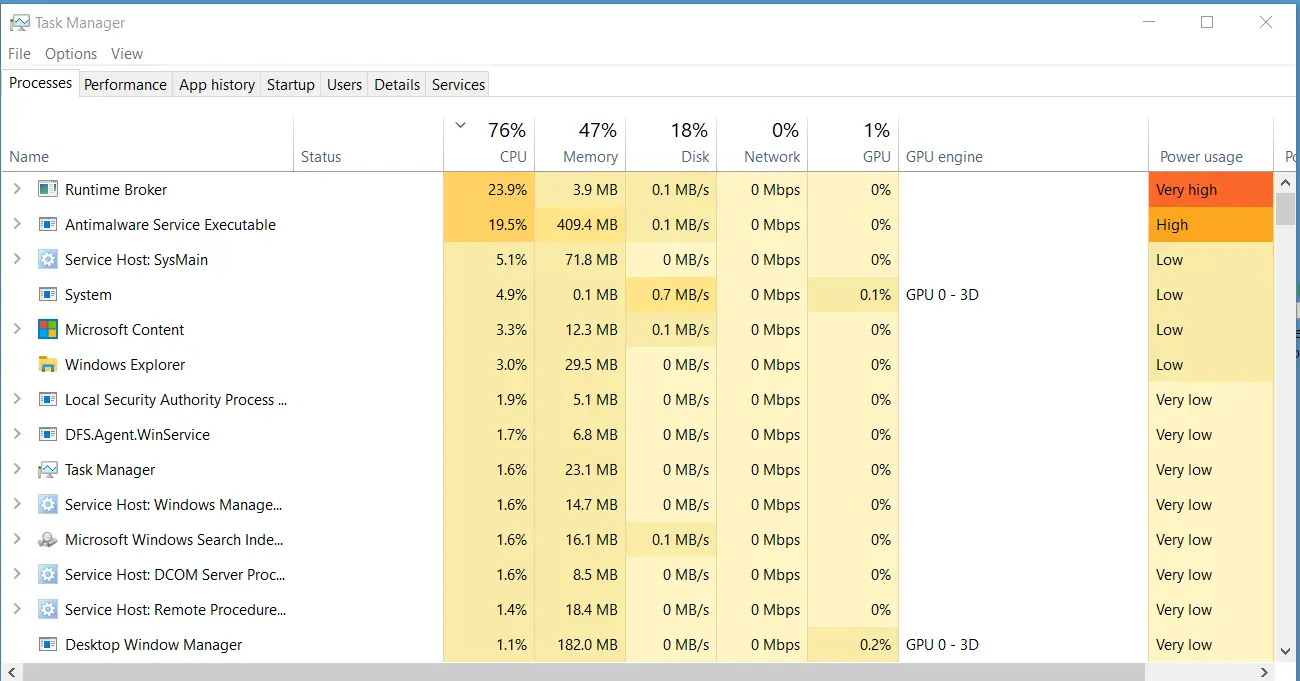
Many users have reported experiencing high CPU usage caused by the Antimalware Service Executable on their Windows 10 systems. This issue can lead to significant performance and system failures, making it important to understand why this occurs and how to address it. In this article, we’ll explore the causes of high CPU usage by the Antimalware Service Executable, its impact on your system, and the steps you can take to resolve this problem.
What is Antimalware Service Executable?
The Antimalware Service Executable (MsMpEng.exe) is a process associated with Windows Defender, the built-in antivirus and antimalware solution in Windows 10. This service is responsible for real-time protection, scanning files for potential threats, and managing the security of your system. While it plays a crucial role in keeping your computer safe, it can sometimes consume excessive CPU resources, leading to system slowdowns.
Key Functions of Antimalware Service Executable
- Real-time protection: Continuously monitors your system for malware and other threats.
- Full system scans: Periodically scans your entire system for potential security issues.
- Definition updates: Regularly updates its database of known threats to ensure your system is protected from the latest viruses and malware.
Why Does Antimalware Service Executable Cause High CPU Usage?
There are several reasons why the Antimalware Service Executable might cause high CPU usage on your Windows 10 system:
1. Real-Time Protection
The real-time protection feature of Windows Defender constantly scans files and processes in the background to protect your system. This can lead to high CPU usage, especially if you are running resource-intensive applications or downloading large files.
2. Full System Scans
Windows Defender regularly performs full system scans to ensure that no threats are present. These scans can be resource-intensive, leading to performance issues and high CPU usage.
3. Large Definition Updates
Windows Defender frequently updates its virus definitions to protect against new threats. Large updates can cause the Antimalware Service Executable to use more CPU and memory resources temporarily.
4. Conflicts with Other Security Software
If you have other antivirus or security software installed on your system, it can conflict with Windows Defender, leading to system failures and increased CPU usage.
5. Corrupted Files or Malware
In some cases, corrupted files or hidden malware can cause the Antimalware Service Executable to behave abnormally, consuming excessive CPU resources.
Impact of High CPU Usage on System Performance
When the Antimalware Service Executable consumes a significant amount of CPU resources, it can lead to various performance and system failures:
1. System Slowdowns
High CPU usage can cause your system to become sluggish, making it difficult to perform basic tasks such as browsing the web, opening applications, or even moving files.
2. Increased Temperature and Fan Noise
When the CPU is under heavy load, it generates more heat, causing your system’s cooling fans to work harder. This can lead to increased fan noise and potentially overheating issues if the system is not adequately cooled.
3. Application Crashes
Resource-intensive applications may crash or freeze if there are insufficient CPU resources available due to the high usage by the Antimalware Service Executable.
4. Reduced Battery Life
For laptop users, high CPU usage can lead to faster battery drain, reducing the overall battery life of your device.
How to Fix High CPU Usage Caused by Antimalware Service Executable
Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to reduce the high CPU usage caused by the Antimalware Service Executable:
1. Adjust Windows Defender’s Scheduled Scan
You can reduce the impact of Windows Defender’s full system scans by adjusting the scan schedule to a time when you’re not actively using your computer. This can be done through the Task Scheduler:
- Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type taskschd.msc and press Enter to open Task Scheduler.
- Navigate to Task Scheduler Library > Microsoft > Windows > Windows Defender.
- Double-click on Windows Defender Scheduled Scan.
- In the Triggers tab, click Edit and adjust the scan schedule to a less disruptive time.
2. Add Antimalware Service Executable to Windows Defender’s Exclusions
Sometimes, excluding the MsMpEng.exe process (Antimalware Service Executable) from Windows Defender’s own scans can reduce CPU usage:
- Open Windows Security by searching for it in the Start menu.
- Go to Virus & Threat Protection > Manage settings.
- Scroll down to Exclusions and click on Add or remove exclusions.
- Click on Add an exclusion, then select Process.
- Type MsMpEng.exe and click Add.
3. Disable Windows Defender’s Real-Time Protection
If you have another antivirus program installed, you might consider disabling Windows Defender’s real-time protection to avoid conflicts and reduce CPU usage. However, keep in mind that this may leave your system vulnerable if your other antivirus software is not as effective:
- Open Windows Security.
- Go to Virus & Threat Protection > Manage settings.
- Toggle off Real-time protection.
4. Check for Malware or Corrupted Files
Sometimes, hidden malware or corrupted files can cause the Antimalware Service Executable to behave abnormally. Use a trusted antivirus program to scan your system for malware, and run the System File Checker (SFC) tool to check for corrupted files:
- Press Win + X and select Command Prompt (Admin) or Windows PowerShell (Admin).
- Type sfc /scannow and press Enter.
- Wait for the scan to complete and follow any on-screen instructions.
5. Update Windows and Drivers
Keeping your Windows 10 system and drivers up to date can help resolve issues related to high CPU usage:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update.
- Click on Check for updates and install any available updates.
- Additionally, check your device manufacturer’s website for any driver updates specific to your hardware.
Advanced Solutions for Persistent Issues
If the above methods do not resolve the issue, consider these more advanced solutions:
1. Install a Third-Party Antivirus Program
If Windows Defender is consistently causing performance issues, you might consider using a third-party antivirus program that is less resource-intensive. Popular options include:
- Bitdefender
- Norton Antivirus
- Avast
2. Disable Windows Defender via Group Policy
For advanced users, disabling Windows Defender via Group Policy can help if you’re planning to use a third-party antivirus program exclusively:
- Press Win + R and type gpedit.msc to open the Group Policy Editor.
- Navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows Defender Antivirus.
- Double-click on Turn off Windows Defender Antivirus and set it to Enabled.
- Click Apply and then OK.
3. Reset or Reinstall Windows 10
If all else fails, consider resetting or reinstalling Windows 10. This should be a last resort, as it will remove all installed programs and could potentially result in data loss. Make sure to back up your important files before proceeding:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery.
- Under Reset this PC, click Get started.
- Choose whether to keep your files or remove everything, and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the process.
High CPU usage caused by the Antimalware Service Executable can be a frustrating issue, but with the right approach, it can be resolved. Whether it’s adjusting scan schedules, excluding processes, or even considering alternative security solutions, taking proactive steps can improve your system’s performance and prevent system failures. By understanding the root causes and applying the appropriate fixes, you can ensure that your Windows 10 system runs smoothly and efficiently.
Remember, maintaining a balance between security and performance is key. Regular updates, system maintenance, and careful monitoring of resource usage can go a long way in keeping your computer in top condition.